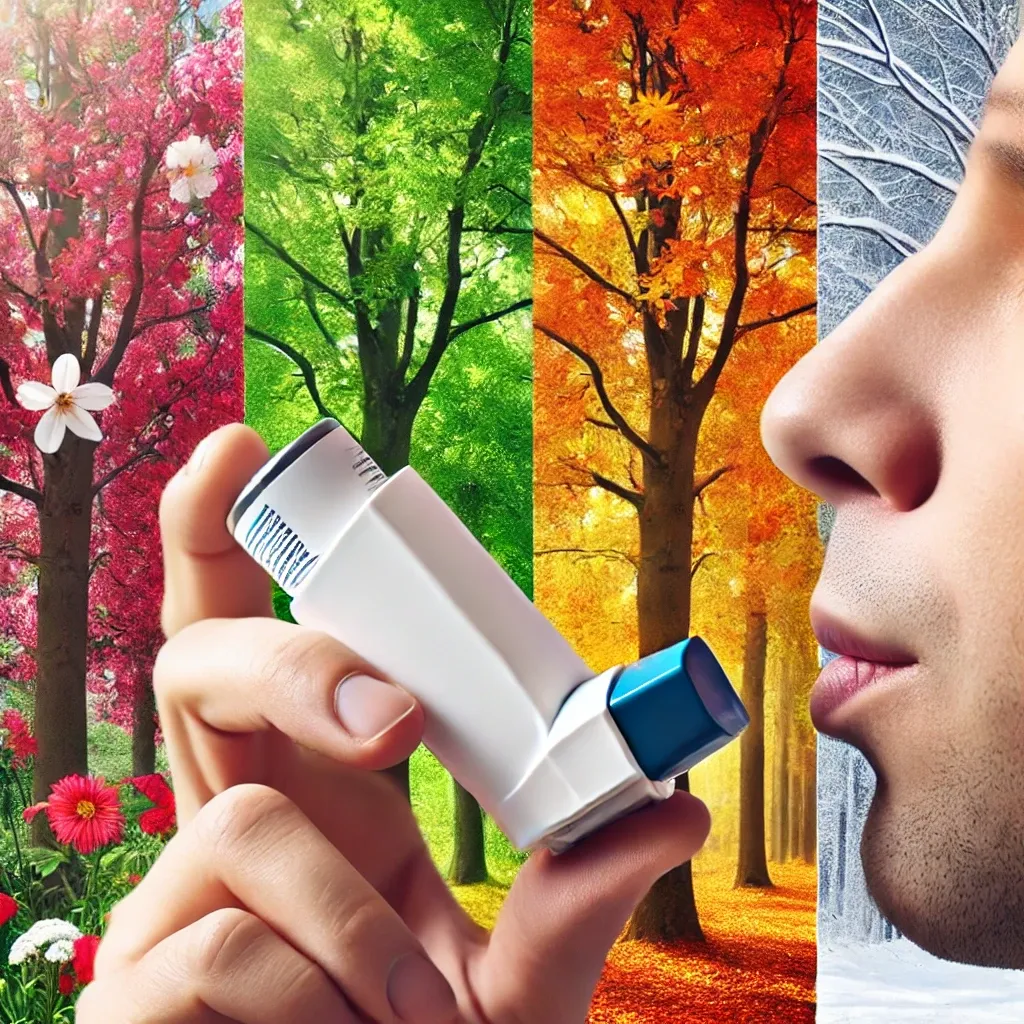
Wondering how seasonal changes impact asthma? Learn about seasonal asthma, its triggers, and how seasonal residues play a role. Is your asthma worsening with the seasons? Read on to find out why and how you can manage it effectively.
Seasonal asthma is a type of asthma that is more pronounced during certain times of the year. It’s essential to understand its causes, triggers, and how it interacts with environmental factors like pollen, air quality, and weather conditions. In this article, we’ll explore what seasonal asthma is, how it differs from other types of asthma, and the specific seasonal triggers like “residue needles” and seasonal cough that can make symptoms worse.
Seasonal Asthma: What It Is and How It Works
Seasonal asthma refers to the exacerbation of asthma symptoms during particular seasons of the year. While asthma itself is a chronic condition characterized by inflammation of the airways, seasonal asthma is influenced by specific environmental factors. Common seasonal triggers include allergens such as pollen, mold, and dust mites. For many people, seasonal asthma typically worsens during the spring and fall, although it can also flare up in the summer and winter under certain conditions.
Key Causes of Seasonal Asthma Exacerbation:
-
Pollen Spring and fall are notorious for pollen production, especially from trees, grasses, and weeds. The inhalation of pollen particles can irritate the airways, leading to inflammation and asthma symptoms.
-
Mold Damp, cool weather in autumn and spring creates perfect conditions for mold growth, which can trigger asthma attacks.
-
Dust Mites During both the fall and spring, dust mites, which thrive in warmer temperatures and humidity, become active.
-
Cold Air Cold air in winter can dry out the airways, making asthma symptoms worse for some individuals.
-
Temperature Extremes Rapid changes in temperature or seasonal shifts in weather can trigger asthma symptoms in susceptible individuals.
For those with seasonal asthma, staying informed about when allergens peak in each season and taking steps to mitigate exposure can help reduce flare-ups.
👉 Learn more about managing seasonal asthma triggers 👈
Seasonal Cough Asthma: Understanding the Connection
Seasonal cough asthma is a specific type of asthma characterized by persistent coughing during certain seasons. This condition often accompanies seasonal asthma, but it primarily manifests as a dry, persistent cough. The cough might worsen at night or with physical activity, especially when exposed to allergens in the air.
Common Triggers for Seasonal Cough Asthma:
-
Airborne Allergens Pollen, dust, and mold spores, which are particularly prevalent in spring and fall, can irritate the airways and cause a dry, persistent cough.
-
Cold Weather In colder seasons, dry air can aggravate the respiratory system, leading to coughing fits.
-
Humidity Changes High humidity can promote mold growth, which can trigger coughing, while low humidity can dry out the airways.
-
Exercise During certain seasons, outdoor activities may expose individuals to allergens, triggering coughing spells.
-
Irritants Smoke from wildfires or other environmental pollutants can also worsen coughing in individuals with seasonal asthma.
If you’re experiencing frequent coughing during a specific season, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider. Seasonal cough asthma can often be managed with medication and lifestyle changes that minimize exposure to known triggers.
👉 Discover how to manage seasonal cough asthma 👈
Seasonal Residue Needles: What They Are and How They Affect Asthma
“Seasonal residue needles” is a term that may refer to the buildup of seasonal allergens such as tree needles or plant debris. During the autumn and winter months, the shedding of tree needles, leaves, and other plant materials can create a layer of allergens on the ground. These residues often mix with dust and pollen, making them even more harmful for individuals with asthma.
Impact of Seasonal Residue Needles on Asthma:
-
Increased Allergen Exposure As leaves and plant debris decay, they release allergens into the air. People with asthma can be more sensitive to these particles.
-
Inhalation of Fine Particles Small particles from pine needles and other plants can irritate the respiratory system and trigger asthma attacks.
-
Heightened Risk During Cleanup Fall yard work or outdoor activities like raking leaves can stir up these allergens, causing exposure to irritants that worsen asthma symptoms.
-
Mold Growth Residue from fallen leaves and other plant matter can promote mold growth, adding another layer of irritation to asthma sufferers.
To avoid exposure to seasonal residue needles, it’s important to limit outdoor activities when pollen counts are high and to take precautions during yard work by wearing a mask and using an air purifier indoors.
👉 Find tips for managing exposure to seasonal residue needles 👈
Conclusion: Managing Seasonal Asthma
Seasonal asthma, seasonal cough asthma, and seasonal residue needles are all interconnected conditions that can significantly impact individuals’ quality of life during certain times of the year. Understanding the underlying causes and triggers of these conditions is key to managing symptoms and improving overall health.
By staying informed about seasonal allergens, taking preventive measures, and following your doctor’s recommendations for managing asthma, you can enjoy a healthier and more comfortable seasonal transition.
As the seasons change, remember: Preparation is the key to breathing easy.